STEP Español
STEP Español is a formative reading assessment system that measures student reading development in Spanish literacy for grades K-3.
STEP Español at a Glance
What is STEP Español?
STEP Español is a formative reading assessment system that measures student reading development in Spanish literacy for grades K-3. STEP Español supports educators in using data to inform instructional decisions for students who are considered Spanish Heritage Language Learners (SHLL). In addition to the assessment, STEP Español provides educators with online data management, online progress monitoring, and a professional learning system.
What is a Spanish Heritage Language Learner (SHLL)?
- SHLL is a subgroup within the English Language Learners (ELL) demographic.
- A SHLL student is raised in a home where a non-English language is spoken, who speaks or understands their heritage language (Spanish), and who is to some degree bilingual in English and the heritage language.
- SHLL represent the largest subgroup of ELLs in the US —78% as of 2015.
What Makes STEP Español Unique From Other Spanish Assessments?
- Unlike most of the Spanish-reading assessments currently available, STEP Español is not a direct translation of its English counterpart. Rather, STEP Español measures students’ abilities against the critical reading milestones that need to be met to achieve proficiency in Spanish, specifically.
- STEP Español uses only authentic Spanish text written to represent a range of authentic cultural experiences and measures student reading progress across the developmental trajectory unique to Spanish literacy.
Why Does K-12 Education Need a Literacy Assessment like STEP Español?
- Historically, primary language support for ELL students focused on the adoption of English as the primary language instead of fostering fluency in both English and their heritage language. This approach supported the narrative that ELL students underachieve because of “poor English skills.”
- Today, there is an ever-growing body of research showing the academic and social advantages of bilingualism. Given this, more schools are embracing and encouraging the development of students’ fluency in both English and their heritage language. This is usually being accomplished through the integration of dual-language and bilingual programs into K-12 education.
- The growing number of K-12 bilingual programs and SHLL population in K-12 schools has increased the demand for formative assessment materials that can meaningfully measure Spanish literacy development. SHLL students attending U.S. schools are either accustomed or have adapted to certain learning practices and protocols unique to the U.S. education system. In order to address these realities, a Spanish-language assessment needs to align with the standards, policies, and practices of a US literacy program.
- For these reasons, UChicago Impact sought to design a culturally and linguistically relevant system for the thoughtful measurement of Spanish reading skills/comprehension at the early grades (K-3).
The STEP Español Framework
STEP Español is grounded in research on the developmental trajectory of Spanish literacy and is designed around four main beliefs:
Assessment of SHLLs should be culturally and linguistically relevant to the student. An assessment should:
- Be grounded in cultural and linguistic relevance—acknowledging that a reader’s diverse literacy practices and bilingual language development develop in tandem.
- Incorporate cultural references and experiences that are relevant and relatable for the reader.
- Include texts that have been developed to reflect the backgrounds of our SHLLs.
- Support teachers in recognizing and discounting any language-related approximations that do not impact comprehension during evaluation. Instead, these reading ‘errors’ are attributable to a reader’s heritage language. For example, a student reading “he say” instead of “he said.”
Reading is sociocultural
- Reading is not just accurately decoding words from a page but is instead a complex interaction between the author, the reader, and the environment.
- Comprehension is rooted in both text-based evidence and schema-based responses.
- SHLLs are encouraged to use their schema to support comprehension and literacy development in Spanish.
- Teachers are supported in learning how to socialize SHLLs into text-accountability conversations, while giving students opportunities to ‘show what they know’ about the text, including drawing upon lived experiences.
Biliteracy and data driven instruction
- Full biliteracy development for SHLL students is attainable for school districts with access to high-quality formative Spanish assessments.
- High quality formative assessments that are grounded in the fundamental principles of a biliteracy framework (oracy, reading, writing and metalanguage) offer educators insight that can support Spanish-language goal-setting in the bilingual classroom and improve teachers’ bilingual instructional practices.
Teacher expertise about language
- There are implications of teachers’ preconceived ideas about language and language learners which impact an evaluation/assessment.
- Since formative assessment relies on teachers’ interpretation of data, teacher understandings about the nature of language (e.g. language can be right and wrong vs. language is a dynamic, holistic system) influence decisions made during evaluation and student outcomes.
- By digging into teachers’ experiences with language development, we can explore and evaluate their own preconceptions.
- It is important to support teachers in reflecting on how they interpret data as it pertains to their students’ Spanish reading development.
Which Reading Abilities Does STEP Español Assess?
STEP Español measures growth across the foundational reading skills needed to achieve reading proficiency in Spanish through a variety of reading activities, including graded reading passages, fluency tasks, developmental spelling lists, alphabet recognition tasks and comprehension-based conversations about texts. The table below lists the discrete components of the assessment in both English and Spanish:
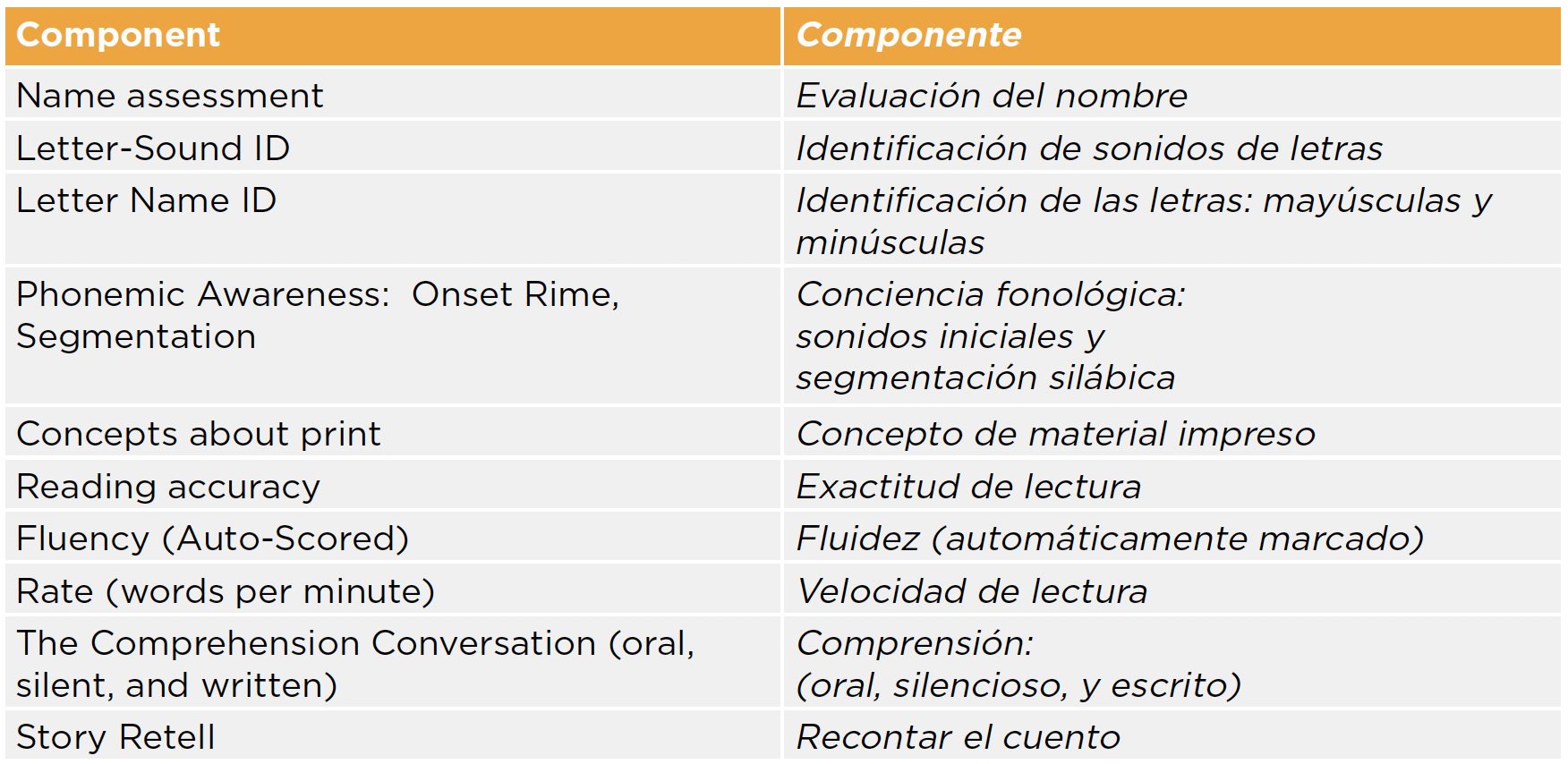
Is STEP Español aligned with an established learning standards framework?
After conducting an extensive review and comparative analysis of four standards frameworks, STEP Español is most closely aligned with the California Common Core State Standards: English/Spanish Language Version (CAL-SPN). These standards share the same core values as STEP Español, including providing SHLLs with the linguistic tools, skills and strategies to become full biliterate and bilingual members of society.
This document is derived from the forthcoming document “The Foundation of STEP Español: What is STEP Español and How Does it Support Spanish-Speaking Students?”.



